Museo
Thyssen-Bornemisza
21 June to 18
September 2016
From
21 June to 18 September 2016, the Museo Thyssen-Bornemisza will be presenting
Caravaggio and the Painters of the North, an exhibition that focuses on
Michelangelo Merisi da Caravaggio (Milan, 1571 – Porto Ercole, 1610) and his
influence on the northern European artists who were fascinated by his painting
and disseminated his style. Curated by Gert Jan van der Sman, professor at the
University of Leiden and amember of the Istituto Universitario Olandese di
Storia dell’Arte in Florence, the exhibition analyses the artist’s legacy and
the wide variety of responses that his work provoked. On display will be 53
paintings, twelve of them by Caravaggio, loaned from private collections,
museums and institutions such as the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, the
Galleria degli Uffizi, Florence, the Hermitage Museum, Saint Petersburg, the
Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam, and the church of San Pietro in Montorio in Rome.
The
exhibition will offer a survey of Caravaggio’s career from his Roman period to
the moving dark paintings of his final years, shown alongside a selection of
works by his most important followers in Holland (Dirk van Baburen, Gerrit van
Honthorst and Hendrick Ter Brugghen), Flanders (Nicolas Régnier and Louis
Finson) and France (Simon Vouet, Claude Vignonand Valentin de Boulogne).
Between
1600 and 1630 more than two thousand artists settled in Rome, of whom a third
were foreigners who transformed the city into an artistic melting-pot. To an
equal or even greater extent than the Italians, the northern European painters
opted to follow Caravaggio’s style for two principal reasons: the lesser
importance of the classical element in the northern pictorial tradition, and
the suitability of Caravaggio’s style for application outside the traditional
context of a studio or drawing academy.
In
the Low Countries and Germanic regions working from life through the
observation of visible elements taken from the surrounding context was a
firmly-rooted tradition. This established a link with the manner of working
characteristic of Caravaggio, whose Lombard origins predisposed him to paint ad
vivum, an approach that artists with a classical training considered inadequate
in that it represented an obstacle to achieving perfection in art. In addition,
most of the Dutch, Flemish and French painters who settled in Rome had received
a basic training in drawing and painting in their native regions and were
particularly interested in rapidly capturing and assimilating new ideas.
Caravaggio’s art thus appealed to them, not only for the possibility of working
from life but alsofor its emphasis on the use of light, shadow and colour.
The
foreign painters were able to assimilate this style into their own without the
restrictions implied by a study program. Caravaggio and the Painters of the
North transports visitors to the era of Michelangelo Merisi da Caravaggio and
the decades following his death, a period particularly rich in masterpieces of
painting and when his fame was still at its height.
The
exhibition opens with two galleries devoted to works by Caravaggio executed
during his time in Rome and which reveal his multi-faceted career. The
following galleries show works by painters from north of the Alps who saw
Caravaggio’s works at first hand. The result of their impressions was
manifested in the widest variety of ways, given that each brought their own
contribution while also seeking out new modes of expression in both religious
and secular art. The last two galleries are devoted to the work of Caravaggio
and his foreign followers in Naples and southern Italy. Caravaggio in Rome
(1592 - 1606)
During
his early years in the city Caravaggio executed paintings that were sold by art
dealers for modest sums. These were genre scenes and still lifes with fruit and
flowers, a speciality that he brought with him from Lombardy.
With Boy bitten by a Lizard of around 1593-95
the artist astonished his contemporaries both for the mimetic qualities of the
vase of flowers and the youth’s melodramatic expression. His depictions of
characters typical of Roman street life, such as
The Fortune Teller of 1595-96 attracted the attention of
painters and collectors.
Earliest admirers in
Rome: Adam Elsheimer and Peter Paul Rubens In 1600, when the German painter
Adam Elsheimer (Frankfurt am Main, 1578 – Rome, 1610) settled in Rome,
Caravaggio was completing his canvases for San Luigi dei Francesi. Peter Paul
Rubens (Siegen, 1577 – Antwerp, 1640) arrived in the city a year later, by
which time Caravaggio had already become widely known. Elsheimer and Rubens
were the first northern European painters to make direct contact with his art.
The
artist’s first patron, Cardinal Francesco Maria del Monte, offered him lodgings
in the Palazzo Madama where Caravaggio painted
The Musicians of 1595-96
and Saint Catherine of Alexandria,
revealing the rapid evolution of
his technique from the brilliant and colourful palette of the former to the
pronounced chiaroscuro of the latter.
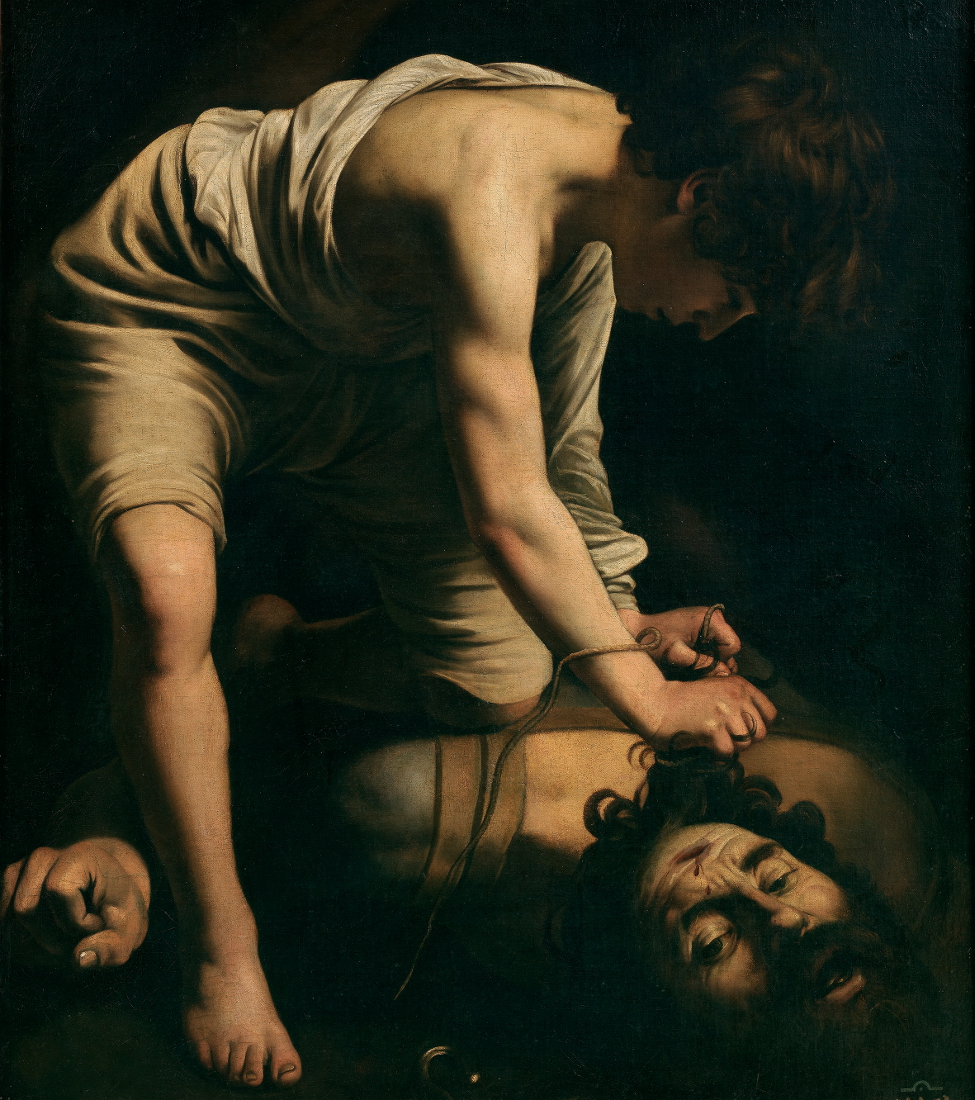
Caravaggio’s
ability to bypass conventions and approach traditional themes with surprising
originality is evident in
David with the Head of Goliath of around 1598-99.
The
years 1596 and 1597 marked a turning point in the artist’s career with the
commission of two canvases –
The Calling of Saint Matthew
and The Martyrdom of
Saint Matthew
- for the Contarelli chapel in the church of San Luigi dei
Francesi, in which Caravaggio combined his preference for painting from life
and the depiction of popular figure types with a moving sense of drama.
From
the moment the work was displayed in public, during the Jubilee of 1600,
Caravaggio became the artist most in demand in Rome, resulting in both public
and private commissions for clients such as Maffeo Barberini, the future Pope
Urban VIII, for whom the artist painted
Caravaggio. The Sacrifice of Isaac, 1603 Gallerie degli Uffizi, Florencia
The Sacrifice of Isaac in 1603
and the banker Ottavio Costa, who commissioned
Saint John the Baptist in
the Desert of 1602.
Caravaggio’s influence is evident in Rubens’s first official commission in Rome
to paint the altarpieces for the basilica of Santa Croce in Gerusalemme. His
interest in Caravaggio is revealed in the powerful lighting of some elements
inthe compositions. In addition, Rubens made use of the Caravaggesque figure
type of the seductive youth with black curly hair in his
Head of a young Man of
1601-02.
During his second period in the city, from 1605 to 1608, he painted
The Adoration of the Shepherds in 1608 using a pronounced chiaroscuro in the area that includes the angels. Rubens also played a key role in the acquisition of the controversial
Death of the Virgin for the Duke of Mantua’s collection. Caravaggio’s painting had been rejected by the Carmelite nuns of Santa Maria della Scala due to the realism employed in the depiction of the Virgin.
Following his return to Flanders, Rubens was again inspired by Caravaggio’s paintings on various occasions, including his celebrated free copy of
The Entombment of Christ, of which a drawing is included in the exhibition (cat. 13).
Artists and art lovers: Quadri da stanzaand quadri d’altare
In addition to owning fifteen works by Caravaggio, the brothers Benedetto and Vincenzo Giustiniani assisted numerous foreign painters to obtain commissions. They also offered accommodation in their house to Gerard van Honthorst (Utrecht, 1592-1656), David de Haen (Rotterdam, 1597(?) – Rome, 1622) and Nicolas Régnier (Maubeuge,ca.1588 – Venice, 1667). Dirck van Baburen (Wijk bij Duurstede, ca.1594 – Utrecht, 1624) was also fortunate in finding a patron shortly after his arrival in Rome, the Spaniard Pedro Cosida, Philip III’s ambassador in the city, whose patronage culminated in the decoration of his chapelin San Pietro in Montorio.
One of Van Baburen’s most admired works of his Roman period is

The Entombment of Christ of 1617 and it is possible that the artist met his patron through José de Ribera who, like him, had arrived in the capital after passing through Parma.
Hendrick ter Brugghen and the Utrecht School
Hendrick ter Brugghen (The Hague (?) – Utrecht, 1629) was the first of the Dutch painters who, following a period in Rome, returned in 1614 to his native country where he introduced Caravaggio’s characteristic subjects and stylistic formulas. In
The Supper at Emmaus of 1616 and
The Calling of Saint Matthew of around 1617-19 (cat. 29) Ter Brugghen adopted Caravaggio’s compositional format using a brilliant palette notable for its subtle gradations of colour and the painstaking depiction of the wrinkles of the skin, drapery folds, tones of the headdresses and the reflection of light on objects.
The return to Utrecht between 1620 and 1621 of Gerard van Honthorst and Dirck van Baburen influenced Ter Brugghen’s stylistic evolution and a healthy rivalry arose between these painters which resulted in an intention to emulate or surpass each other in works such as Boy playing a Recorder(cat. 30) and

The Flute Player, both of 1621, which Ter Brugghen painted as a response to Baburen’s half-length figures of musicians such as

Young Man singing of 1622. Over time Honthorst’s palette became more brilliant and colourful, as evident in paintings such as his
Merry Company of 1622
The French painters in Rome
This gallery displays work by French artists active in Rome between 1610 and 1630, representing a particularly interesting group due to their social and cultural diversity. Among the foreign painters living in the city Simon Vouet (Paris, 1590 – 1649) enjoyed a more privileged position than most. Son of a court painter, he grew up in Paris and had access to the court from an early age. Following a brief period in Venice, he settled in Rome in 1613/14 where he received a regular stipend from the French court. The official nature of his residence in Rome brought him notable prestige in artistic circles and the favour of leading collectors, for whom he executed works such as David victorious over Goliath of 1621.
Claude Vignon (Tours, 1593 – Paris, 1670) also came from a prosperous background as the son of a valet de chambre. Vignon was born in Tours, a habitual place of residence of the French monarchs, and grew up in Paris. Having arrived in Rome in 1609/1610, in 1616 to 1617 he went to Spain and Paris and it is likely that he painted his impressive
Martyrdom of Saint Matthew of 1617 (cat. 36) in France. Vignon’s friendship with Vouet helped his career in Rome.
The situation of these two painters contrasts with the struggle for success on the part of Valentin de Boulogne (Coulommiers, 1531 – Rome, 1632). Some years would pass before the artist found a committed patron in the form of Francesco Barberini. Boulogne’s biographer Giovanni Baglione associated his manner of painting from life with his dissolute lifestyle. Like Caravaggio, Boulogne executed large compositions by painting directly on the canvas. Despite the complexity of his creations, such as

David with the Head of Goliath and two Soldiers of ca.1616-18, there is no evidence that he prepared his compositions with preliminary drawings or studies. Caravaggio and his followers in Naples and southern Italy.
Among the foreign painters living in Naples and
influenced by Caravaggio, two are particularly outstanding: Louis Finson
(Bruges, ca.1580 – Amsterdam,1617) and Matthias Stom ((?) ca.1600 – northern
Italy (?) after 1649). The former is the only northern Caravaggesque painter who
probably knew the artist in person, while Stom was the last of his followers,
producing an oeuvre that reveals Caravaggio’s influence until around 1640.
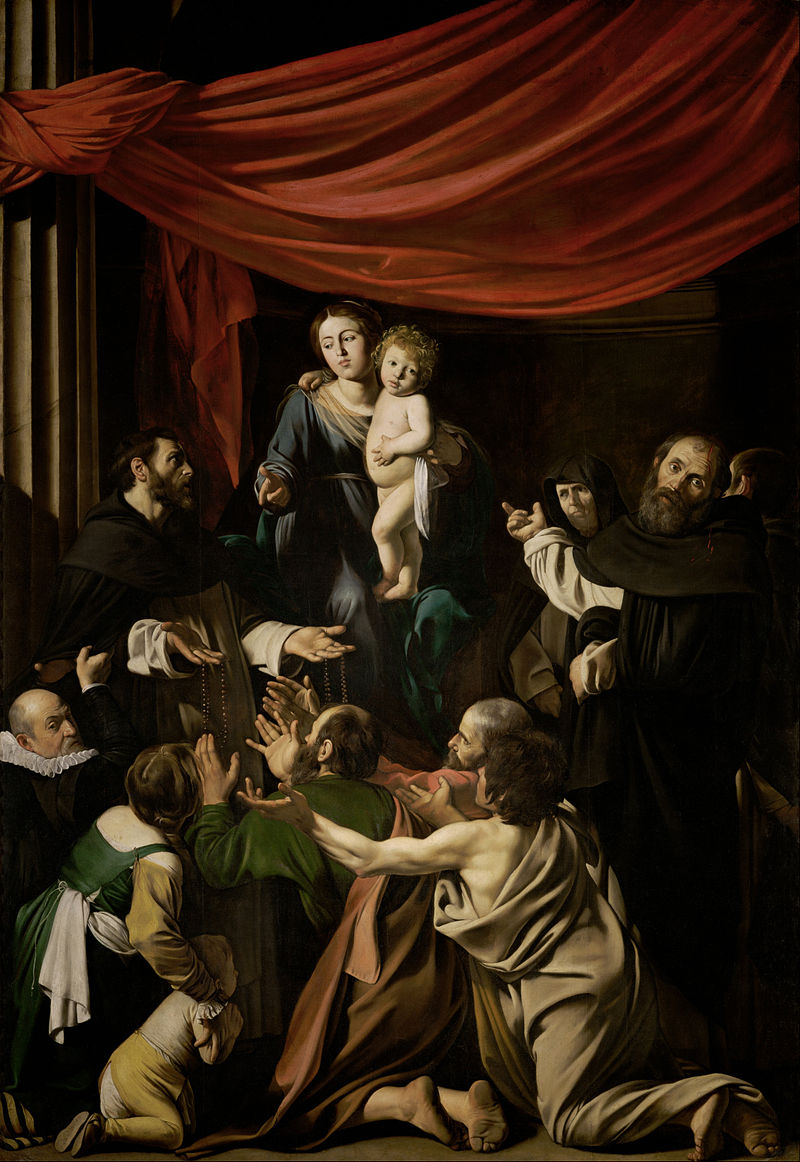
Finson settled in Naples in 1605 where he began to collaborate with Abraham
Vinck, a painter specialising in portraits. It is thought that Caravaggio made
friends with both of them and when he left for Malta in 1607 he entrusted them
with two of his paintings,
Judith and Holofernes
and The Madonna of the Rosary.
In 1612 Finson settled in the south of France where he enjoyed considerable success painting in the style of Caravaggio. He died in Amsterdam in 1617 in the house of his friend and associate Vinck. The paintings that the two took home were the first (and only) originals by Caravaggio that could be seen in the Low Countries.
Twenty years after Finson left Naples, Stom settled in that city. It is not known whether he was born in Amersfoort (near Utrecht) or in Flanders. It is possible that one of Stom’s masters was Gerard van Honthorst who passed on to him his interest in candle-lit scenes.
Stom’s paintings
depicting figures in the immediate foreground were among those that brought him
success in Naples, where he ran his own studio from 1635 to around 1639. In the
1630s Stom’s technique became more fluid and his colours brighter. He moved to
Sicily where he executed various important public commissions.

Judith and Holofernes
and The Madonna of the Rosary.
In 1612 Finson settled in the south of France where he enjoyed considerable success painting in the style of Caravaggio. He died in Amsterdam in 1617 in the house of his friend and associate Vinck. The paintings that the two took home were the first (and only) originals by Caravaggio that could be seen in the Low Countries.
Twenty years after Finson left Naples, Stom settled in that city. It is not known whether he was born in Amersfoort (near Utrecht) or in Flanders. It is possible that one of Stom’s masters was Gerard van Honthorst who passed on to him his interest in candle-lit scenes.

The Flagellation
of Christ of around 1640 is an extremely dynamic composition in which
the life-size figures are illuminated in an exceptionally dramatic manner.
Dominated by the chiaroscuro, this is an extremely theatrical presentation in
which the idealised nude Christ contrasts with the rough appearance of his
torturers in a final echo of Caravaggio.
The exhibition concludes with
Caravaggio.The Martydom of Saint Ursula, 1610 Colección Intesa Sanpaolo. Gallerie d'Italia - Palazzo Zevallos Stigliano, Náp
The Martyrdom of Saint Ursula of 1610, in which Caravaggio depicted himself holding a lance at the moment when the King of the Huns wounds the saint with an arrow. Painted a few weeks before his death, it marks the high point of this final section of the exhibition.

_02.jpg/1024px-La_Diseuse_de_bonne_aventure%2C_Caravaggio_(Louvre_INV_55)_02.jpg)




.jpg/1166px-The_Martyrdom_of_Saint_Matthew-Caravaggio_(c._1599-1600).jpg)
.jpg/800px-Sacrifice_of_Isaac-Caravaggio_(Uffizi).jpg)